A general purpose training procedure that can be applied to a variety of NLP tasks in a zero-shot manner.
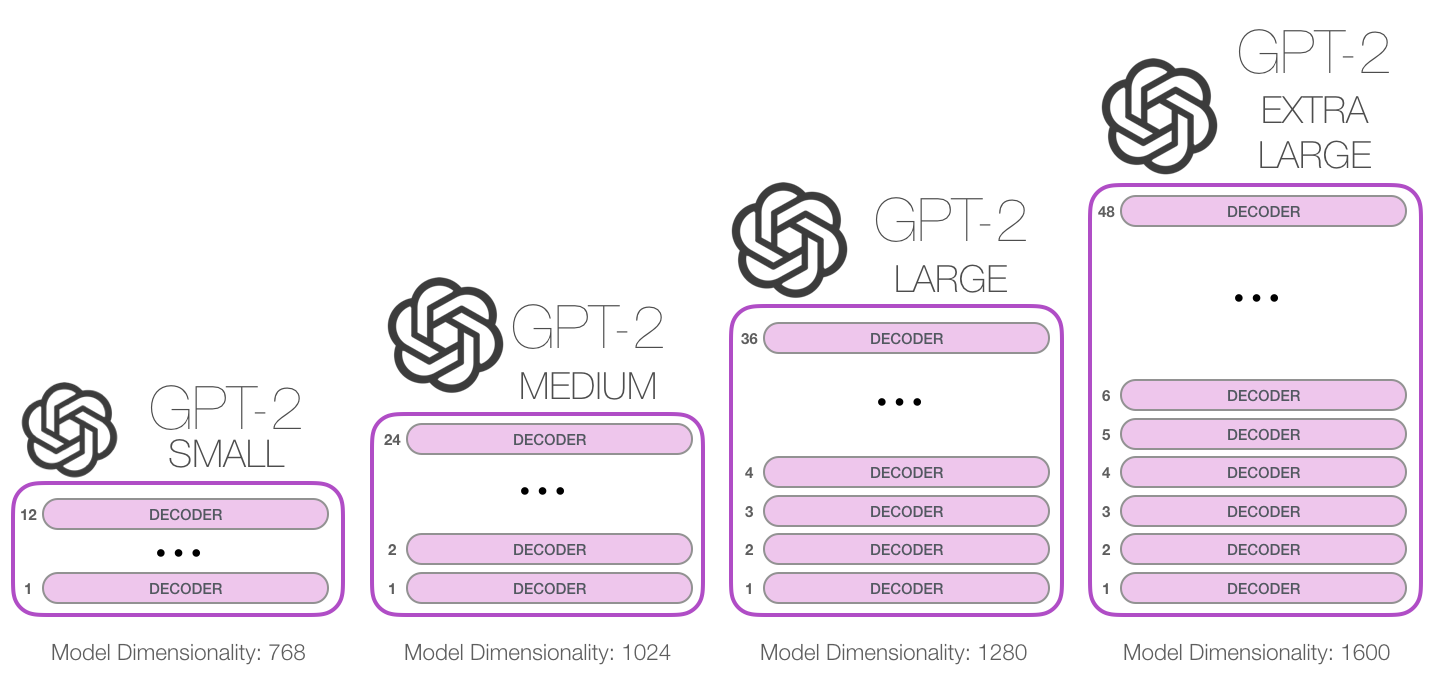
This paper presents a general purpose training procedure that can be applied to a variety of NLP tasks, using task instructions and task input as conditioning factors. A model trained with a massive, diverse, and unsupervised dataset can handle many tasks in a zero-shot manner and typically outperfo...
Read more
11-23-2023
Transformer
Language Model
GPT
paper-note
 XF-Blog
XF-Blog